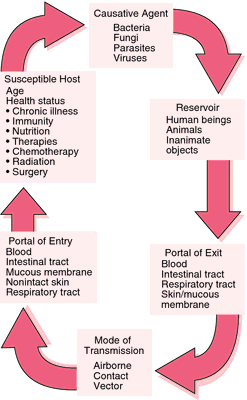
The Cycle Of Infection
The cycle of infection is a good understanding of how infections occur and how they are permitted in the population and how they are spread. The five elements that make p the cycle are:
- Reservoir host
- Means of exit
- Means of transmission
- Means of entrance
- Susceptible host
Reservoir Host is an animal, insect, or human whose body is capable of sustaining the growth of a pathogen. Presence of the pathogen in the reservoir host may cause an infection in the host. A human carrier is reservoir host who is unaware of the presence of the pathogen and so spreads the disease. An infection in the reservoir host may either be endogenous infection which is one in which an abnormality or malfunction in routine body process has caused normally beneficial or harmless microorganisms to become pathogenic or exogenous infection is one that is caused by the introduction of a pathogen from outside the body.
Means of Exit is the pathogens exiting from the reservoir host. Common routes:
- Nose,mouth,eyes, or ears
- Feces or urine
- semen,vaginal fluid, or other discharge through the reproductive tract
- In blood or blood products from open wounds
Means of Transmission is reproduced after it has exited from the reservoir host, pathogen must spread to another host by some mean of transmission either by direct or indirect. Direct transmission occurs when the pathogen moves immediately from one host to another. Indirect transmission is possible only if the pathogen is capable of existing independently of the reservoir host.
Means of Entrance The opening where an infectious disease enters the host’s body such as mucus membranes, open wounds, or tubes inserted in body cavities like urinary catheters or feeding tubes.
Susceptible Host The person who is at risk for developing an infection from the disease. Several factors make a person
more susceptible to disease including age (young people and elderly people generally are more at risk),
underlying chronic diseases such as diabetes or asthma, conditions that weaken the immune system like
HIV, certain types of medications, invasive devices like feeding tubes, and malnutrition.
- Airborne Transmission- can be transmitted to a new host through the air. May enter through respiratory track such as influenza or flu
- Bloodborne Transmission- can enter a new host through contact with blood or blood products. Indirectly through needle sticks,blood transfusions or improperly sterilized dental equipment
- Transmission during Pregnancy or Birth-If mother become infected during her pregnancy she can pass on the pathogen to her fetus. An infection that is present in a child at the time of birth is said to be congenital
- Foodborne Transmission-May be exposed to pathogens by ingesting contaminated food or liquids. Food can be infected by poor hygiene habits.
Means of Entrance The opening where an infectious disease enters the host’s body such as mucus membranes, open wounds, or tubes inserted in body cavities like urinary catheters or feeding tubes.
more susceptible to disease including age (young people and elderly people generally are more at risk),
underlying chronic diseases such as diabetes or asthma, conditions that weaken the immune system like
HIV, certain types of medications, invasive devices like feeding tubes, and malnutrition.
No comments:
Post a Comment